Math2Market GmbH Hall 8 / B26

Exhibitor Profile
MATH2MARKET GmbH is a leader in providing software and consulting solutions for the design of innovative filter media, filter cartridges, filters with housing, and even, room-scale filtration.
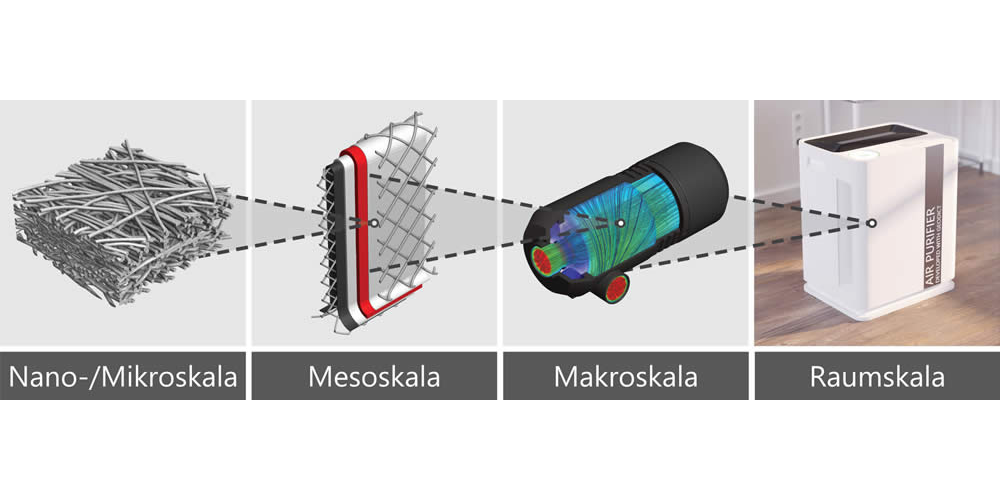
Its GeoDict software uses micro-CT and FIB/SEM scans, CAD models, or user-defined parameters to produce structural models of nonwoven, woven, metal and plastic meshes, synthetic media and papers, ceramics, open-cell foams, membranes, and gradient materials.
GeoDict analyzes and/or predicts pore size distribution, bubble point, fluid flow, pressure drop, particle capture, MPPS, depth filtration, clogging, dust holding capacity, coalescence, and cake formation in the digital models.
Simulations take into account fluid density and viscosity, Brownian motion, inertial impaction, electrostatic forces, adhesion forces, and particle size and mass distribution. The possibilities of digital non-destructive testing and engineering are virtually boundless.
GeoDict's reliable and accurate results cut prototyping and R&D costs and greatly accelerate the engineering of filters and filter media, to boost the competitive edge of our clients.
Products / Markets
Product Index
- Consulting
- Digitale Lösungen
- Filtermedienprüfung
- Prüfdienstleistungen
- Simulation
Market Scope
- Abwasserwirtschaft
- Automobilindustrie
- Batterie Industrie
- Biotechnologie/Biopharmazie
- Chemische Industrie
- Entsalzung
- Filtrations- und Separationsindustrie
- Luft- und Raumfahrtindustrie
- Mineralöl/Öl/Gasproduktion
- Pharmazeutische Industrie
- Textilindustrie
- Umweltschutz
Product Index
- Consulting
- Digital Solutions
- Filter Media Testing
- Simulation
- Testing Services
Market Scope
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Battery Industry (NEW in 2024)
- Biotechnology/Biopharmac. Industry
- Chemical Industries
- Desalination Market (NEW in 2024)
- Environmental Protection
- Filtration and Separation Industry
- Mineral / Oil / Gas Production
- Pharmaceutical Industry
- Textile Industry
- Waste Water Treatment
Product Index
- 咨询
- 数字解决方案
- 模拟
- 测试服务
- 过滤媒介测试
Market Scope
- 汽车工业
- 制药工业
- 化学工业
- 废水处理
- 环境保护
- 生物技术/生物制药业
- 电池行业
- 矿产/石油/天然气业
- 纺织工业
- 脱盐
- 航空航天业
- 过滤与分离工业
Product Index
- اختبار تصفية وسائل الاعلام
- الحلول الرقمية
- خدمات الاختبار
- محاكاة
- مستشار
Market Scope
- إنتاج المعادن والزيوت والغاز
- الصناعات الدوائية
- الصناعة الكيماوية
- الصناعة النسيجية
- تحلية المياه
- صناعات الفلترة وفصل المواد
- صناعة الألبان
- صناعة البطاريات
- صناعة التقنية البيولوجية والبيوصيدلية
- صناعة السيارات
- صناعة الفضاء
- معالجة مياه الصرف
Product Index
- Consultant
- Services de contrôle
- Simulation
- Solutions numériques
- Test de médias filtrants
Market Scope
- Dessalement
- Industrie automobile
- Industrie aérospatiale
- Industrie biotechnologie/biopharmaceutique
- Industrie chimique
- Industrie de filtration et de séparation
- Industrie des batteries
- Industrie laitière
- Industrie pharmaceutique
- Industrie textile
- Productions minérales / pétrolière / du gaz
- Traitement des eaux usées
Product Index
- Consulenza
- Servizi di verifica
- Simulazione
- Soluzioni digitali
- Verifica mezzi filtranti
Market Scope
- Biotecnologie/biofarmaceutica
- Desalinizzazione
- Industria delle batterie
- Produzioni minerali / petrolio / gas
- Protezione ambientale
- Settore aerospaziale
- Settore automobilistico
- Settore chimico
- Settore filtrazione e separazione
- Settore industria tessile
- Settore parafarmaceutico
- Trattamento acque reflue
Product Index
- Ordynacyjny
- Rozwiązania cyfrowe
- Symulacja
- Testowanie mediów filtrów
- Usługi testowania
Market Scope
- Biotechnologia/biofarmaceutyka
- Filtrowanie i separacja
- Ochrona środowiska
- Oczyszczanie ścieków (waste water)
- Odsalanien
- Przemysł akumulatorowy
- Przemysł chemiczny
- Przemysł farmaceutyczny
- Przemysł lotniczy
- Przemysł samochodowy
- Przemysł tekstylny
- Wydobycie minerałów, ropy i gazu
Product Index
- Consultando
- Serviços de teste
- Simulação
- Soluções Digitais
- Testes de meios filtrantes
Market Scope
- Dessalinização
- Ind. de biotecnologia/biofarmac.
- Indústria aeroespacial
- Indústria automóvel
- Indústria de baterias
- Indústria de filtragem e separação
- Indústria farmacêutica
- Indústria leiteira
- Indústria têxtil
- Indústrias químicas
- Produção mineral / óleo / gás
- Tratamento de água de despejo
Product Index
- Имитация
- Обслуживание Тестирования
- Тестирование Фильтрующие материалы
- Цифровые решения
- консалтинг
Market Scope
- Авиакосмическая промышленность
- Автомобильная промышленность
- Аккумуляторная промышленность
- Биотехнология / Биофармацевтическая промышленность
- Добыча минералов/ нефти/ газа
- Молочная промышленность
- Отрасль фильтрации и сепарирования
- Очистка сточных вод
- Текстильная промышленность
- Фармацевтическая промышленность
- Химическая промышленность
- опреснение
Product Index
- Consultante
- Pruebas de medios filtrantes
- Servicios de Pruebas
- Simulación
- Soluciones digitales
Market Scope
- Desalinización
- Industria aeroespacial
- Industria de baterías
- Industria de la automoción
- Industria de la biotecnología/biofarmacéutica
- Industria de la filtración y la separación
- Industria de los productos lácteos
- Industria farmacéutica
- Industria textil
- Industrias químicas
- Producción de minerales / petróleo / gas
- Tratamiento de aguas residuales
Product Index
- Danışmanlık
- Dijital Çözümler
- Filtre ortamı test
- Simülasyon
- test Hizmetleri
Market Scope
- Akü Endüstrisi
- Atıksu Arıtma
- Biyoteknoloji/Biyoeczacılık Endüstrisi
- Filtrasyon ve Ayırma Endüstrisi
- Havacılık Endüstrisi
- Kimya Endüstrisi
- Mineral / Petrol / Gaz Üretimi
- Otomotiv Endüstrisi
- Tekstil Endüstrisi
- Tuzdan arındırma
- Çevre Koruma
- İlaç Endüstrisi
Product Index
- 디지털 솔루션
- 시뮬레이션
- 여과재 테스트
- 컨설팅
- 테스트 서비스
Market Scope
- 광물 / 석유 / 가스 생산
- 담수화
- 배터리 산업
- 생명공학/생물 약제학 산업
- 섬유 산업
- 여과 및 분리 산업
- 자동차 산업
- 제약 산업
- 폐수 처리
- 항공우주 산업
- 화학 산업
- 환경 보호
Product Index
- Consulting
- シミュレーション
- デジタルソリューション
- 濾過材試験
- 試験サービス
Market Scope
- バイオテクノロジー・バイオ医薬品産業
- 化学工業
- 医薬品業界
- 汚水処理
- 濾過および分離技術工業
- 環境保護
- 繊維業界
- 脱塩
- 自動車産業
- 航空宇宙産業
- 鉱物・石油・ガス生産
- 電池産業
What's new
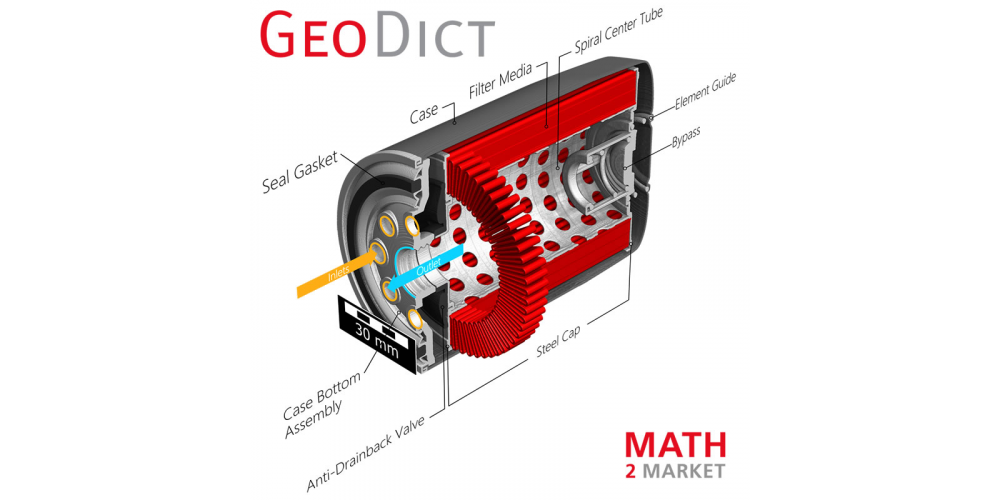
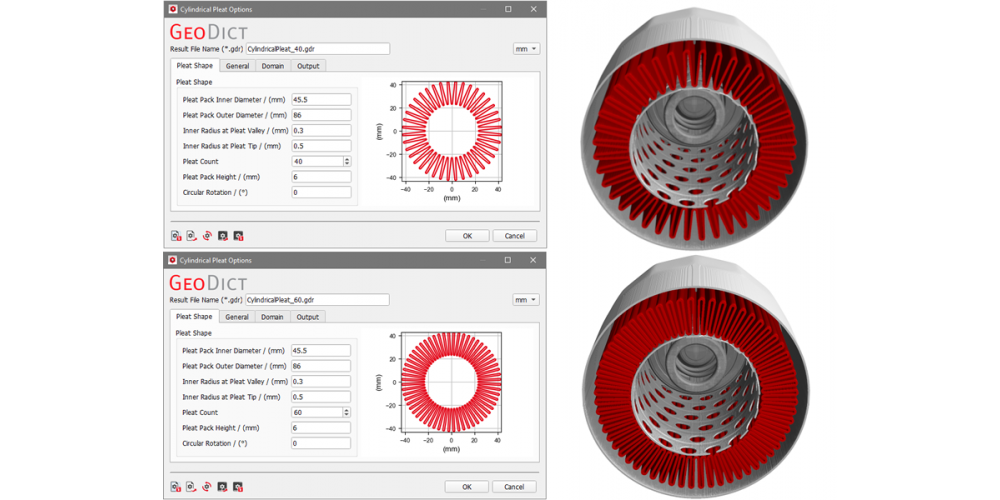
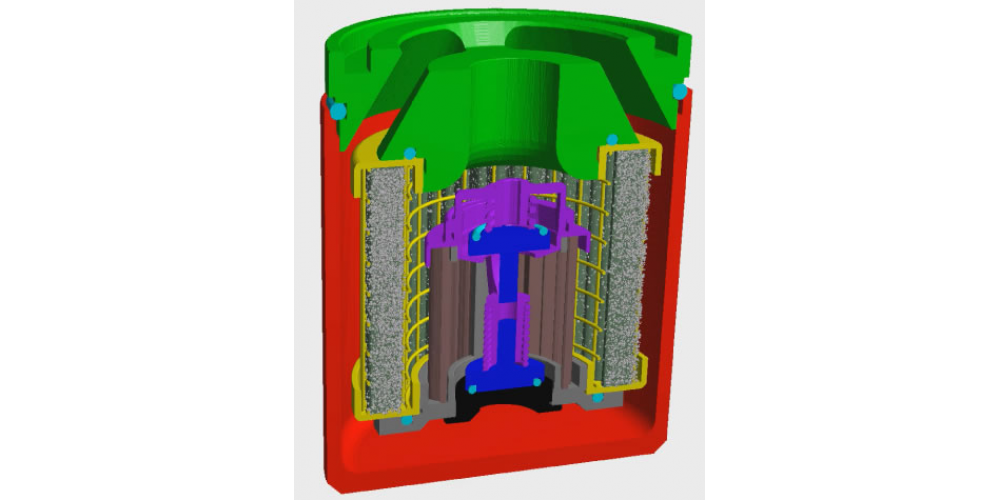
Digital design and virtual switching of cartridges to increase filter performance – the new GeoDict software feature
Computer-Aided-Design (CAD) is of keen interest to simulate flow and filtration on filters with cartridges. However, performing systematic simulations on different geometrical setups requires the generation of these structures as CAD individually and the import of each sample separately.
A new feature in the GeoDict software allows to generate a variety of cartridges with changing pleat count, pleat thickness, and number of porous layers, and digitally switch them inside the housing. Starting now, it is easy and quick to find the ideal configuration between filter area and pleat count for cartridges and their housing, regarding their local minimum pressure drop and many filtration relevant parameters.
This digital test of the performance of filter prototypes circumvents the need for expensive, trial-and-error manufacturing and testing phases, since only promising prototypes undergo measurements at the testbench. These systematic simulations with varying geometries or flow rates may be run simultaneously in cloud applications to further increase the productivity, fit customers requests, and decrease time-to-market.
What's new
GeoDict in ASTM E3278-21 International Standard
The simulation software GeoDict is presented in the ASTM E3278-21 international standard to digitally perform bubble point pressure testing of woven wire filter cloth.
Traditionally, the pore diameter is calculated using the measured pressure based on the Young-Laplace equation for the equilibrium of the gas pressure and surface tension forces. However, this equation is only for the perfect model (cylindrical pore, thin film with contact angle of 0°, isopropanol wetting liquid) and must be corrected by either the actual contact angle or a tortuosity factor for the filter cloth.
Alternatively, according to ASTM E3278-21, the software-based calculations of the PoroDict module of GeoDict are obtained through the non-circular cross-section of the bottle neck through-path of the filter cloth. This improves correlation and is able to generate a specific correction factor for each different filter cloth specification.
The ASTM E3278-21 standardizes software-based calculations of pore size through bubble point computations performed with the PoroDict module.
PoroDict quantitatively characterizes pore size, percolation path, tortuosity, bubble point pressure, and other parameters of the pore space, such as Pore Size Distribution (Granulometry and Porosimetry), Chord Length Distribution, open and closed porosity, and geodesic tortuosity.
Math2Market software products are a worthwhile new technological strategy, used by internationally renowned manufacturers in the filtration industry to optimize processes, to cut prototyping and R&D costs, to accelerate the design of filter and filter media greatly, and to boost their competitive edge.
What's new
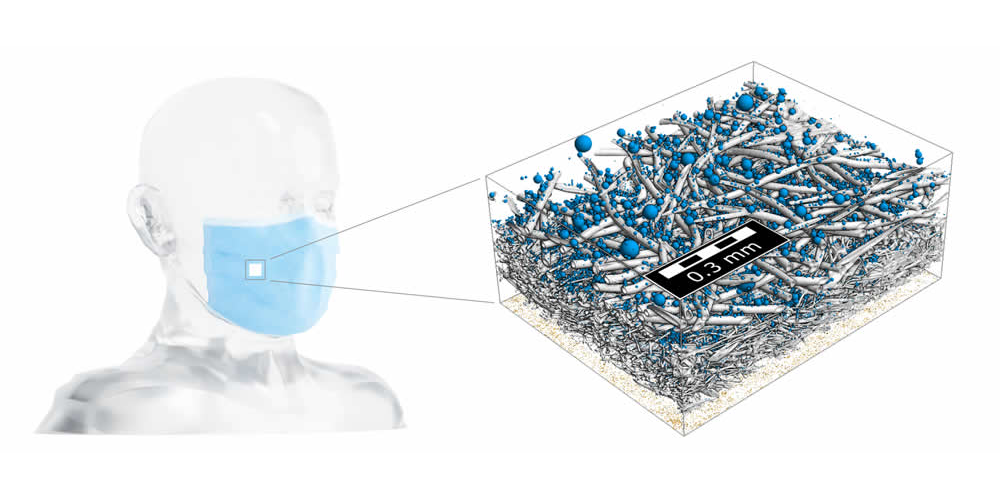
Modeling, simulation, and optimization of filter media for protective face masks
In answering the global demand for safe personal protective equipment and the need for faster development and optimization of face masks, we demonstrate in a short video how GeoDict software is applied to design, model, simulate, analyze and optimize the filter media to improve the filter characteristics of face masks.
This unique digital workflow with GeoDict represents an efficient, sustainable and state-of-the-art methodology for digital R&D material design for porous media, explicitly shown here for a filter medium as an example.
These reliable quantitative simulations are the way to a time and cost saving approach for the development of new filter materials and filters with superior lifetime and performance. Development phases can be significantly accelerated thanks to shortened development times. The innovations can be developed much more easily by obtaining digitally unique insights and rich information about material prototypes and their properties, even before manufacturing them.
What's new
The GeoDict simulation software of Math2Market is part of the ASTM E2814-18 international standard
MATH2MARKET GmbH is a leader in providing software and consulting solutions for the design of innovative filter media, and for the improvement of filtration processes from its location in Kaiserslautern, Germany, near Frankfurt. Math2Market’s team, with an extensive research background, develops and supplies the GeoDict® software for R&D in numerous industries. For the filtration industry, Math2Market supports pioneering digital filter development and design to improve pressure drop, efficiency, and lifetime of filters, while at the same time greatly reducing, or even eliminating, expensive and time-consuming experimental testing.
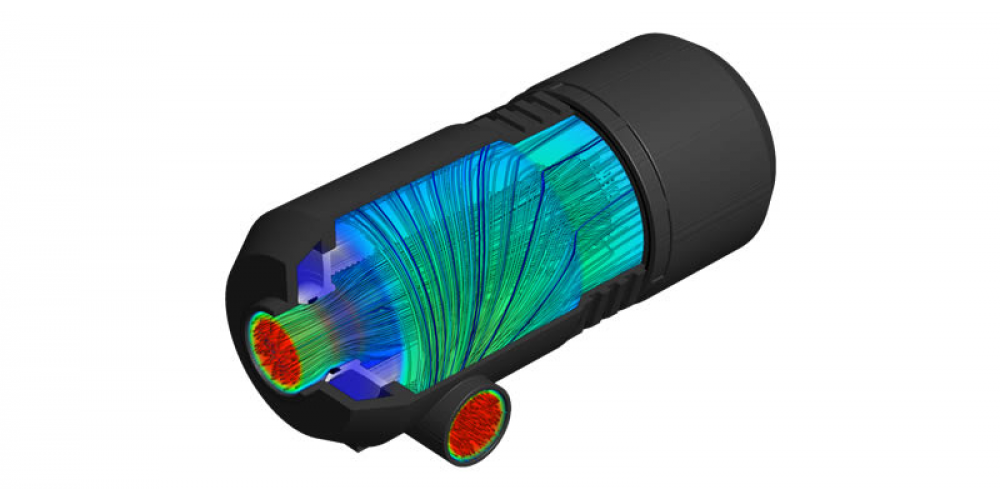
Math2Market’s software GeoDict® only needs user-defined specifications, micro-CT and FIB/SEM images of filter media, or CAD models of filter elements to produce structural models of filter elements, pleats, and media (nonwoven, woven, metal and plastic meshes, synthetic media and papers, ceramics, open-cell foams, membranes, gradient materials…). Then, it analyzes pore size distribution, bubble point, fluid flow, pressure drop, particle capture, MPPS, depth filtration, clogging, dust holding capacity, and cake formation in the digital models. Gas filtration (air: DPF, HVAC) or liquid filtration (oil filter, hydraulic filters, sludge filtration, water, blood…) processes are simulated taking into account fluid density and viscosity, Brownian motion, inertial impaction, electrostatic forces, adhesion forces, and particle size and mass distribution. The possibilities of digital non-destructive testing are virtually boundless.
Math2Market software products are a worthwhile new technological strategy, used by internationally renowned manufacturers in the filtration industry to optimize processes, to cut prototyping and R&D costs, to accelerate the design of filters and filter media greatly, and to boost their competitive edge.
Youtube Videos
-
GeoDict - A part of the ASTM International Standard E2814-18
GeoDict User Meeting 2020 - Innovations in GeoDict 2021
DE #digitization #GeoDict GeoDict for Filtration - Filter Life-Time Prediction
Optimizing the location of air purifiers with GeoDict
Introduction to workshop on simulation of exhaust treatment
Workshop on Simulation of particulate flows through whole filter with housing
Design, modelling, simulation and optimization of filter media for face masks with GeoDict